Summary
Electromagnetic Stirring (EMS) is a transformative technology that significantly enhances casting quality and production efficiency in modern metallurgical operations. By using controlled magnetic fields to stir molten metal, EMS ensures better thermal uniformity, chemical homogeneity, and finer grain structure—resulting in stronger, defect-free cast products. It also minimizes issues such as segregation, porosity, and shrinkage, which improves overall product reliability. Beyond quality, EMS boosts casting speeds, increases yield, reduces energy consumption, and lowers maintenance costs, making it a high-value investment for manufacturers. As industries move toward automation and smarter production systems, EMS emerges as a crucial tool for achieving consistent, high-performance casting. With the right engineering expertise, EMS helps plants maximize output while maintaining world-class quality standards.
In modern metal manufacturing, quality, precision, and efficiency are the benchmarks that define success. As industries push for higher performance materials and seamless production processes, the demand for advanced technologies has grown significantly. One such transformative technology is the Electromagnetic Stirrer (EMS)—a highly effective solution used in continuous casting and metallurgical processes to enhance product quality, reduce defects, and boost overall productivity.
At Samrudhi Engineers, we specialize in delivering reliable industrial and engineering solutions that help manufacturers achieve operational excellence. In this blog, we explore the engineering benefits of EMS, how it enhances casting quality, and why integrating EMS into metallurgical operations can significantly increase output and yield.
1. What is Electromagnetic Stirring (EMS)?
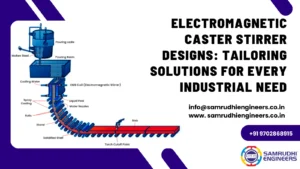
Electromagnetic Stirring is a non-contact stirring method used during the continuous casting of steel and various alloys. Unlike mechanical stirrers, EMS uses rotating or oscillating magnetic fields generated by induction coils placed around the mould or secondary cooling zone.
When these magnetic fields interact with molten metal, they create Lorentz forces, which induce controlled stirring patterns inside the metal bath. This movement of molten metal ensures uniform distribution of heat, chemicals, and microelements—ultimately improving metallurgical quality.
Key Types of EMS:
Mould EMS (M-EMS) – Installed around the mould to improve initial solidification.
Secondary EMS (S-EMS) – Used in the secondary cooling zone to control columnar-to-equiaxed grain transition.
Final EMS (F-EMS) – Applied in the final solidification zone to reduce centerline segregation and porosity.
Each type of EMS plays a unique role in ensuring the cast product is free from internal and surface defects.
2. How EMS Improves Casting Quality
Quality consistency in casting is largely influenced by the behavior of molten metal during solidification. Electromagnetic Stirring significantly improves this behavior and helps manufacturers produce defect-free, structurally sound slabs, blooms, and billets.
Below are the key ways EMS elevates casting quality:
2.1 How EMS Improves Casting Quality
One of the primary challenges in casting is uneven temperature distribution in molten metal. Localized temperature variations can cause premature solidification, hot spots, or weak areas in the final product.
EMS ensures:
Uniform heat distribution
Reduced temperature gradients
Optimized solidification rates
This results in superior metallurgical structure and fewer thermal defects.
2.2 Improves Chemical Homogeneity
Without proper stirring, various alloying elements or impurities distribute unevenly inside the molten metal. This leads to:
Segregation defects
Non-uniform chemical composition
Reduced strength and durability
EMS creates a steady stirring action that mixes alloying elements thoroughly, ensuring the metal solidifies with uniform chemistry, which directly leads to improved tensile strength, ductility, and performance.
2.3 Produces Finer and Consistent Grain Structure
Grain structure determines the mechanical properties of any metal. EMS promotes:
Conversion from columnar to equiaxed grains
Finer and more uniform grain size
Reduced formation of unwanted dendrites
A fine grain structure means:
Higher mechanical strength
Improved surface quality
Better machinability and weldability
This makes the final product more reliable and suitable for high-precision industrial applications.
2.4 Minimizes Internal Defects
Internal defects like porosity, centerline shrinkage, macro-segregation, and inclusions are critical quality concerns in casting.
EMS significantly reduces:
Gas entrapment
Centerline segregation
Shrinkage cavities
Blowholes and inclusions
By maintaining a controlled flow and stable meniscus level, EMS ensures the cast product is structurally sound and free from internal voids.
3. How EMS Increases Casting Output & Productivity
Beyond improving quality, EMS provides substantial gains in productivity, making it a crucial tool for high-volume manufacturing units.
3.1 Higher Casting Speeds
With better temperature regulation and improved solidification conditions, EMS allows manufacturers to achieve:
Faster casting speeds
Higher throughput per heat
Reduced process downtime
Plants can increase their output without compromising quality—a vital benefit for large-scale steel and alloy manufacturers.
3.2 Improved Yield and Reduced Rejections
Casting defects often lead to:
Rework costs
Scaling losses
Scrap generation
Downtime during inspections
Since EMS minimizes defects at the source, manufacturers enjoy:
Higher yield
Lower rejection rates
Better ROI per cast
This directly improves profitability and enhances production planning accuracy.
3.3 Reduced Heat and Energy Consumption
EMS optimizes solidification and minimizes unnecessary superheating of metal. This leads to:
Lower heat-related losses
Reduced fuel/electricity intake
Efficient use of resources
Energy savings translate to substantial cost reductions and a more sustainable manufacturing process.
3.4 Lower Maintenance Costs
Mechanical stirrers introduce:
Wear and tear
Contamination risks
Frequent maintenance needs
Since EMS is non-contact and uses electromagnetic force, it ensures:
Minimal mechanical wear
Longer equipment lifespan
Reduced maintenance downtime
This reliability is a key factor in maintaining continuous and consistent casting cycles.
4. Engineering Advancements Enabled by EMS
EMS is not just a quality-enhancing tool—it brings modern engineering benefits that empower industries to adopt smart manufacturing practices.
4.1 Integration with Automation & Industry 4.0
Modern EMS systems can be integrated with:
Automated process controls
Real-time temperature sensors
Casting speed controllers
Predictive maintenance software
This enables smart decision-making and enhances operational efficiency.
4.2 Compatible with Simulation & Modelling Tools
In advanced foundries, EMS-assisted casting is often simulated through software such as:
THERCAST
ANSYS
MAGMA
These tools help optimize:
Coil design
Magnetic field strength
Stirring direction
Flow patterns
This results in scientific, data-driven casting strategies that yield superior results.
4.3 Customizable for Different Alloys & Casting Sizes
EMS systems can be tailored for:
Billet casting
Bloom casting
Slab casting
Specialty alloy casting
Whether manufacturers produce mild steel, stainless steel, high-carbon steel, or non-ferrous alloys, EMS can be calibrated to achieve the required metallurgical properties.
5. Why Manufacturers Are Adopting EMS Rapidly
EMS has become a preferred solution across the global metallurgical industry because it offers:
- Higher quality with fewer defects
- Higher productivity and casting speeds
- Lower operating costs
- Enhanced structural and mechanical properties
- Better consistency across production batches
For industries aiming for world-class quality and efficiency, EMS is no longer an option—it is a necessity.
6. Electromagnetic Stirring: A Smart Investment for Future-Ready Casting
As markets evolve, the demand for defect-free, high-performance materials continues to rise. Manufacturers who integrate EMS are better prepared to meet these expectations with confidence.
Key Outcomes of EMS Integration:
Superior product quality
Reduced production losses
Streamlined casting operations
Better market competitiveness
7. Samrudhi Engineers: Your Partner in Advanced Industrial Solutions
At Samrudhi Engineers, we are committed to supporting industries with high-performance engineering solutions. Our expertise in the industrial domain ensures that we help clients adopt the most advanced technologies—including EMS systems—that elevate operational excellence.
We understand the critical role of casting quality and productivity in today’s manufacturing landscape. Through our solutions, service quality, and engineering insights, we empower industries to achieve:
Greater precision
Operational reliability
Higher productivity
Cost-effective performance
If your manufacturing facility aims to improve casting quality, boost productivity, and reduce defects, EMS technology is the ideal path forward—and Samrudhi Engineers is here to guide you.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic Stirring (EMS) has revolutionized the casting process by offering unmatched improvements in metallurgical quality, structural consistency, and production throughput. With benefits like thermal uniformity, chemical homogeneity, fewer defects, higher speed, and reduced operating costs, EMS stands out as one of the most impactful innovations in the metal casting industry.
As industries move toward automation and smart manufacturing, integrating EMS becomes an essential step in staying competitive and future-ready.
With the right partner—such as Samrudhi Engineers—manufacturers can unlock the full potential of EMS and achieve superior casting performance.