Summary
This blog delves into the importance of Electromagnetic Caster Stirrers (EMS) in continuous casting processes and how Samrudhi Engineers provides customized EMS solutions for various industrial needs. It explains the different types of EMS—Mould (M‑EMS), Strand (S‑EMS), Final (F‑EMS), Linear (L‑EMS), and Slab EMS—along with their applications, features, and benefits. The blog highlights Samrudhi’s engineering expertise, design precision, energy efficiency, and end-to-end support. It also explores future trends like AI-driven stirring systems and showcases a real-world case study, positioning Samrudhi Engineers as a trusted partner for advanced EMS solutions.
Introduction
In industries like steel manufacturing, continuous casting plays an essential role in delivering high‑quality billets, blooms, and slabs. Yet, achieving uniform solidification, reducing defects like porosity or segregation, and ensuring consistent mechanical properties remain critical challenges.
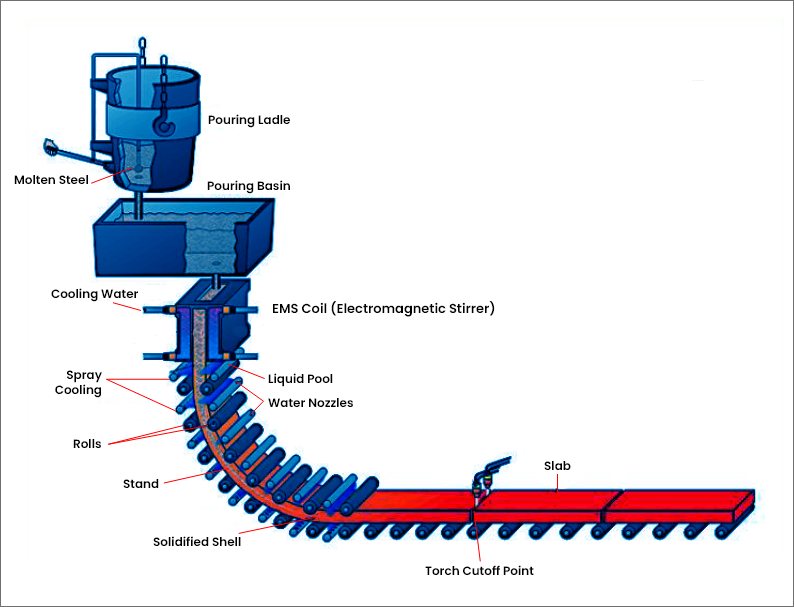
Why Electromagnetic Stirring Matters in Continuous Casting
Control of Centerline Segregation: Molten steel often develops chemical inhomogeneity along the centerline during cooling. EMS induces stirring in the liquid metal to promote uniform solute distribution. The result: reduced segregation and stronger, more reliable steel.
Reduced Internal Defects: By enhancing fluid motion and refining solidification, EMS minimizes the formation of voids, cracks, and porosity—dramatically improving structural integrity.
Improved Surface Finish: Stirring helps ensure smoother solidified surfaces, reducing the need for costly downstream finishing or grinding.
Increased Productivity, Lower Waste: Uniform quality means less scrap, greater yield, and more efficient operations—from energy to throughput.
Samrudhi Engineers: A Trusted Partner in Customized EMS Design
Specialized Expertise: Since their inception in 2012, Samrudhi Engineers has led the industry in designing and manufacturing electromagnetic stirrer coils, offering rewinding, repair, and full EMS solutions for continuous casters and ladle applications.
ISO 9001:2015 Certified and Reputable: Their manufacturing processes adhere to global quality standards, and they’ve built a solid reputation serving major clients including TATA Power, JSW, ABB, JSL and more.
Comprehensive Capabilities: From design and manufacturing to installation, real‑time controls, and support, Samrudhi Engineers consistently delivers turnkey EMS systems optimized for each caster setup.
Types of electromagnetic caster stirrers
A. Mould Electromagnetic Stirrer (M-EMS/MEMS)
Location: Positioned at the mould level, where the metal first solidifies.
Primary Purpose: To ensure homogeneity from the outset; vital for eliminating surface and sub-surface defects.
Design Aspects:
Can be installed inside the mould (internal design) or outside (external design).
Cooling is essential; may use the mould’s system or a dedicated one.
Must operate reliably in a high-temperature, water-cooled environment.
B. Strand Electromagnetic Stirrer (S-EMS/SEMS)
Location: Below the mould, in the secondary cooling zone.
Primary Purpose: Maintains the benefits of stirring as the steel continues to solidify, combating centerline segregation and microstructural inhomogeneity.
Design Aspects:
Installed directly on the strand housing, sometimes with roller-type (in-roll) variants.
Cooling and robust construction are essential for reliability in the harsh environment.
C. Final Electromagnetic Stirrer (F-EMS/FEMS)
Location: Further downstream, near the end of solidification.
Primary Purpose: Enhances grain refinement and reduces internal porosity; critical for demanding steel grades and thick sections.
Design Aspects:
Designs may leverage long iron cores and rotating magnetic fields for deep, uniform stirring.
Often installed externally, using dedicated water-cooling systems.
Key Features of Samrudhi’s EMS Design Approach
a. Precision Magnetic Field Control
Their systems leverage advanced electromagnetic control to adjust stirring intensity in real‑time—ensuring optimal performance for different steel grades and caster speeds.
b. Process Customization
Samrudhi Engineers tailors the EMS design—frequency, coil winding pattern, cooling specs, power input—to fit the specific geometry and metallurgical requirements of each caster.
c. Energy Efficiency
Utilizing modern power electronics and efficient coil design, Samrudhi’s systems achieve stirring performance with lower energy consumption, reducing operational cost and carbon footprint.
d. Real-Time Monitoring & Control
Integrated sensors and control units allow operators to monitor field strength, temperature, and current casting conditions—adjusting parameters during operation to maintain quality.
e. Lifecycle Support & Maintenance
Beyond manufacturing, their complete service package includes installation, rewinding, regular servicing, technical consultation, and spare part supply to maximize system uptime.
Case Study Highlight: High‑Performance Slab Casting Installation
In early 2025, Samrudhi Engineers delivered an advanced EMS stack for a leading slab caster installation:
Challenges: Ultra‑high casting speeds, tight metallurgical tolerances, and a push for energy‑efficient, sustainable operation.
Solution: A phased EMS deployment including mold and final stirrers with precise field control and cooling, coupled with smart hardware and operator dashboards.
Outcomes:
Marked reduction in centerline segregation and internal porosity
Noticeable surface finish improvement
Productivity gains through reduced downtime and scrap
Energy savings from optimized power usage and field control
Designing the Right EMS System: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Process Review: Define caster type (billet, slab, bloom), steel grade, casting speed, and quality goals.
Field Mapping & Coil Placement: Choose M‑EMS, S‑EMS, F‑EMS, or L‑EMS based on where stirring is most effective.
Cooling & Installation Strategy: Decide between mold water use, separate water loops, or modular external coils.
Control System Integration: Specify sensors, interfaces, and PLC or operator panels for real‑time control.
Energy & Field Simulation: Simulate electromagnetic fields and energy draw to optimize coil winding and power electronics.
Manufacturing & Quality Assurance: Fabricate coils per ISO standards, conduct inspection, install, and validate performance on site.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic caster stirrer systems mark a significant technology leap in addressing quality, efficiency, and yield challenges in continuous casting. Through precision design, real‑time control, and customized engineering, Samrudhi Engineers has established itself as a leading provider of EMS technology for industrial metallurgy.
Whether you operate a modern slab caster or are retrofitting batch casting lines, Samrudhi’s tailored solutions—from mould to final or linear EMS—can elevate your product quality, maximize uptime, and reduce operational costs.